2.2.3. Reserve Requirements
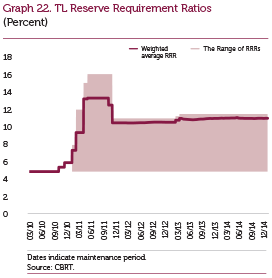
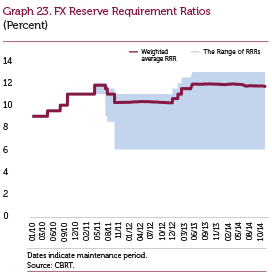
The CBRT continues to use reserve requirements as a monetary policy and macroprudential instrument. By the end of 2014, the weighted average reserve requirement ratios for Turkish lira and FX are 11 percent and 11.7 percent, respectively (Graphs 22 and 23).
To simplify the structure of reserve requirements, an approach to directly involve items subject to reserve requirements was adopted as of 2014 instead of subtracting certain items from total domestic liabilities in calculating liabilities subject to reserve requirements. With this approach, effective as of the calculation period of 17 January 2014, many small items that have no direct effect on the monetary policy and reduce the efficiency of operational process were exempted from the scope of the required reserve liability.
Through the ROM, not only did total reserves register an increase, but also the effects of potential volatilities in external financing conditions on the economy were contained.
Considering the global market developments and the operational procedures for reserve requirements, the CBRT limited the type of currency maintained within the ROM to USD, effective as of 1 August 2014.
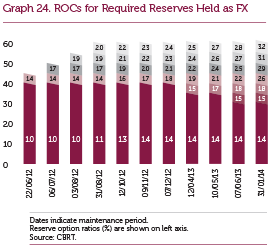
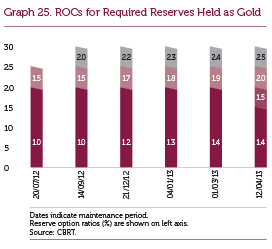
At the beginning of 2014, in order to enhance the efficiency of the ROM, FX reserve option coefficients (ROC) were revised for the upper tranches. By the end of 2014, the coefficients corresponding to the last tranches of the FX and gold reserve options stood at 3.2 and 2.5, respectively (Graphs 24 and 25).
Banks and financing companies use the ROM facilities widely and consistently. As of the maintenance period of 19 December 2014, the utilization ratio of the FX facility became 86 percent, and that of the gold facility reached 87 percent across the sector. Banks can also maintain standard gold for precious metal deposit accounts, the utilization ratio of which is around 75 percent.
To spur balanced growth and domestic savings, the CBRT started to remunerate required reserves of banks and financing companies maintained in Turkish lira, as of November 2014. The CBRT press release dated 21 October 2014 announced that, starting from 2015, as a way to encourage core liabilities, financial institutions whose ratio of deposits and equity to loans are higher than the sector average will be remunerated at a higher rate unless they worsen their own situation.
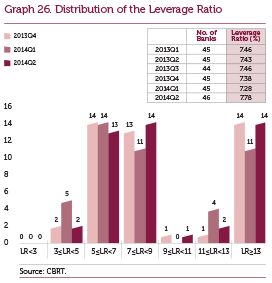
The leverage-based reserve requirement regulation that aims to boost the resilience of the banking sector to shocks by containing its indebtedness continued to be implemented with all of its aspects in 2014. The leverage ratio of the sector realized around 7.8 percent as of June 2014 (Graph 26). The data pertaining to April-June 2014 suggest that the banking sector’s leverage ratio, having a stable course, is well above the minimum ratio of 3 percent set by the Basel III regulation and 4 percent set by the CBRT for 2014. An analysis by banks reveals that no bank is required to hold additional reserve requirements.
