The CBRT Payment Systems consist of systems developed and operated by the CBRT such as Interbank Payment System (EFT), the Retail Payment System (RPS), the Electronic Securities Transfer System (ESTS) and Auction System (IHS), along with an instant payment system called the Instant and Continuous Transfer of Funds (FAST).
In 2021, the value of transactions conducted via the EFT totaled TRY 102.46 trillion, while the average daily transaction amount was TRY 411.52 billion. The number of transactions carried out via the system was approximately 3 million in 2021, corresponding to 12,600 payment messages processed per day on average. The amount of transactions settled via the EFT in 2021 increased by approximately 16.8% compared to the previous year (Chart 2.5.1.1).
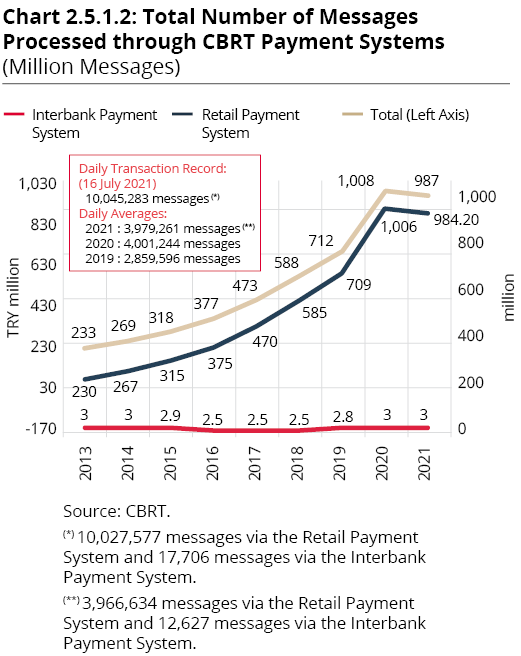
The total amount of messages processed via the RPS in 2021 was TRY 36.90 trillion, corresponding to transactions of TRY 148.22 billion per day on average. 984 million transactions were conducted via the system in 2021, and the average daily number of messages processed was 3.95 million. The highest daily number of transactions as of end-2021 was registered at 10 million on 16 July 2021. The number of settlements carried out via the RPS in 2021 has declined by 2.1% since 2020 (Chart 2.5.1.2) due to the activation of the FAST System on 8 January 2021, which led to a shift in retail payments from the RPS to the FAST System.
The average daily number of messages processed in the auction system was 816.
The number of participants in the CBRT’s Payment Systems stood at 55 by the end of 2021.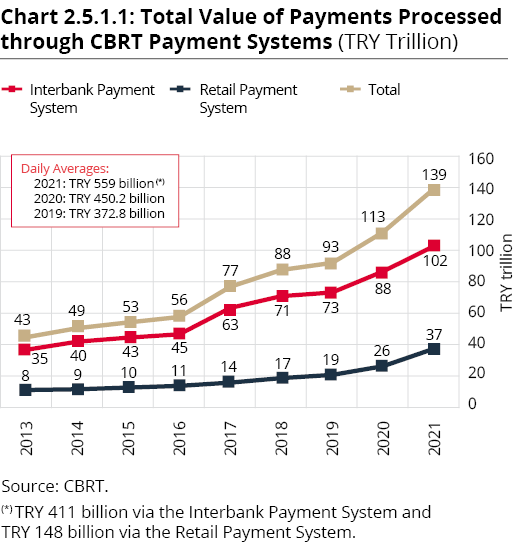
The instant payment system FAST, developed by the CBRT and put into effect on 8 January 2021, is one of the major endeavors of the CBRT to modernize Türkiye’s payment systems infrastructure to support innovative methods of executing businesses. With the FAST System, which operates 24/7, end-to-end transfer of retail payments is enabled within seconds, and the parties are instantly notified.
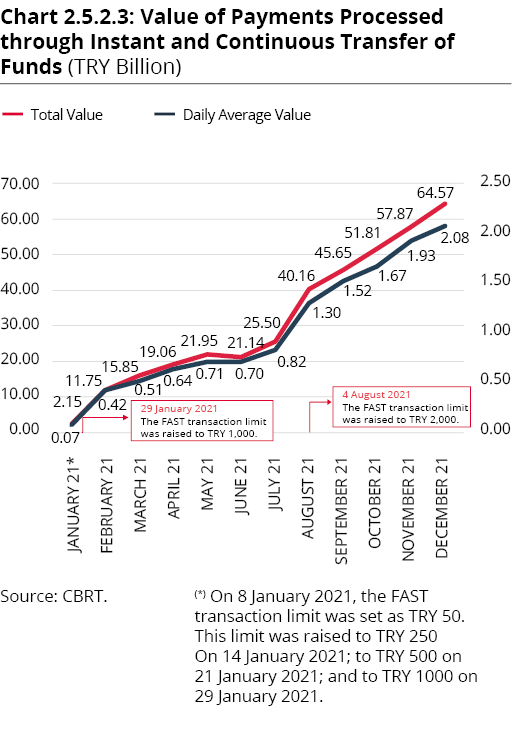
The upper limit for transaction amount was initially set as TRY 50, and gradually increased to TRY 2,000 by August 2021. Thanks to the layer services built on the system, payments can be initiated using telephone numbers, ID numbers, e-mail addresses or QR code without the need of data such as the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) and name‑surname.
Through this system and also other value-added services that will become operational, it is expected that people’s use of cash will decline and unregistered transactions will be averted.
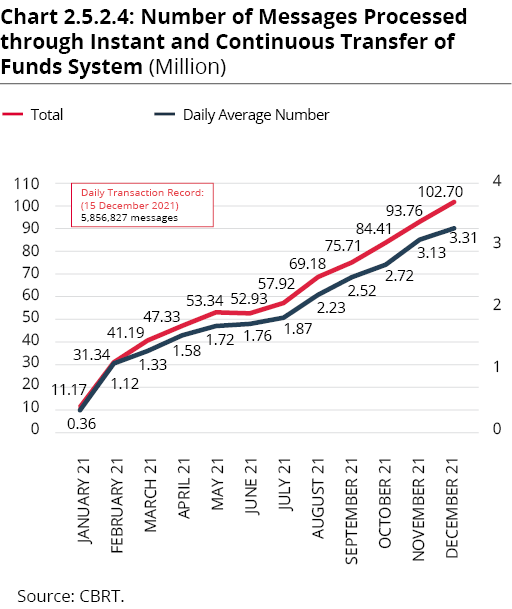
In 2021, the messages processed within FAST totaled TRY 377.46 billion, corresponding to TRY 1 billion per day on average (Chart 2.5.2.3). In 2021, the number of transactions conducted via the system was 721 million and messages processed daily amounted to 2 million on average. The highest daily number of transactions as of end-2021 was registered on 15 December 2021 at 5.85 million (Chart 2.5.2.4).
As of 31 December 2021, the number of participants of the system was 23. On the other hand, applications for participation in the system by payment and electronic money institutions have been received since June 2021, and the evaluation process continues.
The Regulation on the Generation and Use of TR QR Code in Payment Services (TR QR Code Regulation) entered into force following its publication in the Official Gazette on 21 August 2020. It set the rules and principles for the use of TR QR code in payment services as well as the liabilities of the parties to payments made via the QR code within the scope of the Law regarding Payment and Securities Settlement Systems, Payment Services and Electronic Money Institutions (Law No. 6493).
With the TR QR Code Regulation, various liabilities were imposed on the CBRT, Interbank Card Center (ICC), to ensure interoperability between payment service providers and uniformity in execution in payments via QR code under Law No. 6493.
In this context, the CBRT produced guidelines that include workflows regarding the use of TR QR Code in payments with cards, in the FAST System and in mobile payment services, and published them on the CBRT web site. They are: Guidelines for TR QR Code Technical Principles and Rules for ICC (Payments with Card), Guidelines for TR QR Code Technical Principles and Rules for the FAST, and Guidelines for TR QR Code Technical Principles and Rules in Mobile Payments, respectively.
The QR Code Routing System (KYS) was established at the ICC to ensure the transfer of QR codes and the information contained therein between payment service providers in payments via the TR QR Code. The rules and principles for the functioning of the KYS including the operating rules, participation terms and tariffs for the QR Code Routing System were published on the CBRT website under “the Rules for the QR Code Routing System”.
Instructions for Use of the TR QR Code Logo, which set the method to use the TR QR Code logo to ensure that clients are informed in accordance with the display format determined by the CBRT, was announced to the public on the CBRT website in February 2021.
Finally, in 2021, the CBRT carried out studies for the follow-up of the sector and guidance when necessary, and closely monitored the efforts made by payment service providers and other relevant parties to adapt to the TR QR Code transactions. Given the pandemic conditions, payment service providers collaborated with a limited number of third parties to carry out TR QR Code transactions, and efforts to improve the TR QR Code in the sector were delayed. This could have caused high costs due to the limited time to transition to the TR QR code, and the deadline was extended to 30 June 2022 to ensure that payment service providers can adapt to the provisions of the TR QR Code Regulation in the switch to the TR QR Code.
The “Amendment to the Communique on the International Bank Account Number” (No. 2008/6) No. 2021/5 was published in the Official Gazette dated 5 August 2021 and numbered 31559. Accordingly, the scope of the Communique on IBAN was expanded to cover all the payment service providers stated in Article 13 of the Law No. 6493. With this amendment, payment service providers other than banks and the Postal and Telegraph Corporation (PTT) were enabled to generate an IBAN for customer accounts that are subject to money transfer. However, the obligation to generate an IBAN was not imposed on payment service providers other than banks for customer accounts that are subject to money transfer, unless otherwise provided by the system rules of the payment system in which they take part as a participant within the scope of Law No. 6493.
The Regulation on the Rules and Principles for Retail Customer Arbitration Committee of the Turkish Association of Payment and Electronic Money Institutions, which aimed at evaluating and resolving disputes between members and customers, without prejudice to the provisions of the Law No. 6502 on Consumer Protection of 7 November 2013 as well as rights to appeal entrusted by other laws was approved by the CBRT on 5 August 2021. It was prepared in accordance with the subparagraph (c) of the first paragraph of Article 6 of the Statute of the Association of Payment and Electronic Money Institutions of Türkiye (TÖDEB), which was enforced with the Presidential Decision No. 2678 published in the Official Gazette dated 28 June 2020 and numbered 31169, in accordance with the Professional Ethical Principles document of the Payment and Electronic Money Institutions of the Payment and Electronic Money Institutions Association of Türkiye, which sets the professional principles and standards to apply to the staff of member organizations, as well as the subparagraph (ğ) of the same paragraph.
Enactment of the Regulation on the Disuse of Crypto Assets in Payments
It was considered that the use of crypto assets in payments may cause non-recoverable losses for the parties to the transactions and they include elements that may undermine the confidence in methods and instruments used currently in payments. Accordingly, pursuant to the authority vested by the CBRT Law No. 1211 and the Law No. 6493, the “Regulation on the Disuse of Crypto Assets in Payments” was entered into force with publication in the Official Gazette No. 31456 on 16 April 2021.
In line with the objectives of this Regulation, payment service providers shall not adopt business models that directly or indirectly use crypto assets in the provision of payment services and in the issuance of electronic money, and shall not provide any services related to such business models. Payment and electronic money institutions shall not intermediate the fund transfers from and to the platforms providing services of trading, custody, transfer or issuance related to crypto assets. All these rules aim at preventing crypto assets from harming the development of the payments area.
Enactment of the Regulation on Payment Services and Electronic Money Issuance and Payment Service Providers and the Communiqué on Information Systems of Payment and Electronic Money Institutions and Data Sharing Services of Payment Service Providers in the Payment Services Area
The CBRT has carried out secondary regulation studies to contribute to the formation of a competitive and constantly improving payments ecosystem in tandem with the evolving requirements of the day. Regarding these studies, the needs of the sector, consumer complaints, international standards, best practices and regulations in other countries were taken into account. Those issues that are believed to contribute to the effective, smooth and uninterrupted operation of the institutions were included in the regulations in a way so as not to limit the development of financial innovation.
Accordingly, provisions and arrangements previously included in the “Regulation on Payment Services and Electronic Money Issuance and Payment Institutions and Electronic Money Institutions”, which was enforced upon its publication in the Official Gazette No. 29043 on 27 June 2014, were also taken into account. To enforce new arrangements that will meet the needs of the sector, the “Regulation on Payment Services and Electronic Money Issuance and Payment Service Providers” based on Articles 12, 14, 14/A, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 and 26 of the Law No. 6493 entered into force following its publication in the Official Gazette No. 31676 on 1 December 2021. In this regulation, details for offering payment order initiation and account information services were set; rules regarding minimum equity liability and collateral mechanism were developed to ensure that payment and electronic money institutions have a financially sound structure; and additional provisions were introduced to ensure healthy relations between institutions and the parties with which they have legal relations within the scope of representation and outsourcing services. Moreover, establishment of a workplace registration system was stipulated to prevent fraud, and measures were taken to prevent potential disruptions in the operation permit process.
“The Communiqué on Information Systems of Payment and Electronic Money Institutions and Data Sharing Services of Payment Service Providers in the Payment Services Area” entered into force upon its publication in the Official Gazette No. 31676 on 1 December 2021. This Communiqué lays down the rules and principles to be complied with by payment service providers with regard to open banking in the payment services area and information systems to be used by payment and electronic money institutions simultaneously with payment services and electronic money. Within the scope of the Communiqué, processes that will employ the remote communication tool were detailed and existing rules regarding the information systems that organizations use to carry out their activities were reviewed. Moreover, requirements to be met for outsourcing for strong identity authentication and information systems were addressed; and additional provisions were introduced about increasing privacy through data safety and data sharing services used in payment services.
Data Sharing in the field of Payment Services (Payment Initiation Service and Account Information Service)
To foster cooperation across the entire ecosystem for the implementation of Data Sharing Services in the field of Payments (DSSP), a well-attended working group for was established with the participation of banks, which are members of the Banks Association of Türkiye (TBA) and the Participation Banks Association of Türkiye (PBAT) as well as TÖDEB member organizations and companies operating in the area of open banking. This working group held 16 meetings in total in 2021. Following the publication of the secondary regulations, the roadmap for implementing DSSP was shared with the participants at the meeting held on 24 December 2021. Based on the transitional provisions in the regulations, the studies to be completed in 2022 were explained at the meeting.
Accordingly, payment service providers holding a payment account and ranking among the top ten participants in terms of the total number of payment transactions carried out in the CBRT Payment Systems in 2020 were obliged to connect to the API Gateway provided by the Interbank Card Center (the BKM) before 1 December 2022 to utilize payment initiation account information services. A list of these banks was also presented.
The working group continued to develop DSSP API Principles and Rules (API Standards) in line with the regulatory work. By the end of 2021, DSSP Introductory Document version 1.0, DSSP API Principles and Rules (API Standard) version 1.0, DSSP Payment Order Initiation Service Provider (PISP) Customer Experience version 1.0, and DSSP Account Information Service Provider (AISP) Customer Experience version 1.0 documents were completed.
Three applications for operating licenses for other activities that payment and securities settlement system operators may offer in addition to their principal activities were approved and published in the Official Gazette. One system operator’s application for change in the collateral mechanism prepared by the system operator to manage liquidity and credit risks was approved. One payment systems’ application for transfer of shares was approved.
As of 31 December 2021, there were eight payment systems and four securities settlement systems operating in Türkiye pursuant to Law No. 6493.
Two companies’ applications for operating licenses were approved and published in the Official Gazette. Five institutions’ applications for expansion of activities were approved and published in the Official Gazette. Six institutions’ applications for transfer of shares were approved, whereas two institutions’ applications for transfer of shares were rejected. The operating license of one institution was revoked, and the revocation was published in the Official Gazette.
As of 31 December 2021, there were 30 payment institutions and 26 electronic money institutions operating in Türkiye pursuant to Law No. 6493.